- Understand what is DME in medical billing and why it matters in 2026
- Learn best practices to reduce denials and stay audit-ready
- Discover how automation improves accuracy and reimbursement
- See how modern DME billing software supports growth and compliance
Durable Medical Equipment (DME) billing is one of the most specialized (and often misunderstood) areas of healthcare revenue cycle management (RCM). It sits at the intersection of clinical necessity, documentation accuracy, payer policy, and evolving healthcare regulations.
In 2026, DME billing continues to play a vital role for providers who supply essential equipment like wheelchairs, oxygen systems, CPAP machines, hospital beds, and other life-enhancing tools patients depend on. Getting this process right is crucial not only for financial sustainability but also for ensuring patients receive the equipment they need without delay or frustration.
This comprehensive guide will explain what is DME billing, why it matters, and the best practices providers should adopt in 2026 to optimize revenue, minimize denials, and operate compliantly in a shifting regulatory environment.
What is DME Medical Billing? An Overview
Durable Medical Equipment (DME) refers to medical devices and supplies that:
- Are designed for repeated use,
- Serve a medical purpose,
- Typically benefit a patient outside of a clinical setting (e.g., at home), and
- Are prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Examples include wheelchairs, walkers, oxygen systems, CPAP machines, and certain wound care supplies.
DME billing is the process of submitting claims to payers (such as Medicare, Medicaid, or commercial insurers) to receive reimbursement for supplying these items to beneficiaries. Unlike routine medical billing, DME billing involves unique coding requirements, specific documentation expectations, and often complex eligibility and rental rules that set it apart from other types of claims.
In essence, DME billing connects the clinical prescription for life-improving equipment with the financial mechanisms that ensure providers are compensated and patients remain covered.
Why DME Billing Matters in Healthcare
Though seemingly technical, accurate DME billing carries real clinical and financial impact:
Patient Access: Errors can delay delivery of essential equipment, affecting patient health and satisfaction.
Revenue Integrity: Frequent denials, audits, and recoupments stemming from billing mistakes can severely disrupt cash flow for suppliers.
Compliance Risk: Regulatory scrutiny of DME claims is increasing, especially under Medicare, making compliance a core business priority rather than a back-office concern.
Ultimately, DME billing isn’t just paperwork — it’s a foundation for sustainable care delivery.
How the 2026 DME Billing Landscape Is Evolving
As we head deeper into 2026, the DME billing environment continues to shift in response to broader policy trends:
Competitive Bidding Program Expansion
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is broadening and re-introducing the DMEPOS Competitive Bidding Program in more categories, requiring suppliers to adapt pricing and billing strategies.
Heightened Audit and Compliance Focus
Medicare and other payers are employing advanced analytics to identify patterns of improper billing and fraud. This increases the likelihood of pre-payment reviews and post-payment audits.
Digital Transformation
The industry is accelerating the adoption of electronic claim submission, automated eligibility verification, AI-assisted coding, and integrated documentation systems to reduce manual errors.
Rental and Payment Rule Changes
Updated rules around rental caps, replacement frequency limits, and documentation standards are reshaping how claims are submitted and reimbursed.
Providers who stay ahead of these changes position themselves for stronger financial performance, less administrative burden, and improved payer relationships.
DME billing in 2026 demands precision. With stricter audits, evolving payer rules, and expanded competitive bidding, even small errors in documentation or coding can delay patient care and significantly impact revenue.
Proactive DME billing strategies drive better outcomes. Providers that invest in automation, compliance readiness, and staff education are better equipped to reduce denials, accelerate reimbursement, and stay ahead of regulatory change.
Core Components of DME Billing
To excel in DME billing, it helps to understand its fundamental parts:
1) Eligibility Verification
Before equipment is dispensed, it is essential to verify that the patient’s insurance:
Is active
Covers the prescribed equipment, and
Has any required authorizations in place.
This step should be done both at the time of order and on delivery day to capture any benefit changes that could affect reimbursement.
2) Accurate Coding
DME claims use HCPCS Level II codes, which are alphanumeric identifiers that classify the specific item provided. Using incorrect, outdated, or generic codes increases the risk of denial.
Modifiers, such as NU (new equipment), RR (rental), or KX (medical necessity met), provide additional context and must be applied correctly.
3) Documentation and Medical Necessity
Documentation supports why the equipment was needed. This typically includes:
Physician orders,
Clinical notes,
Proof of delivery, and
Any prior authorization forms required by the payer.
Medicare and many commercial insurers scrutinize claims closely for evidence that the equipment was medically necessary for the patient’s care.
4) Claim Submission
Electronic claim submission streamlines processing and typically results in faster payments. Ensure all documentation is attached and accurate before hitting submit.
5) Denial and Audit Management
Tracking denials and analyzing root causes is a key best practice. Common reasons for denials include:
Incorrect coding,
Incomplete documentation,
Eligibility mismatches,
Modifier errors.
Responding to denials with prompt appeals supported by accurate documentation is essential to protect revenue.
Best Practices for DME Billing in 2026
To succeed in today’s increasingly complex DME billing landscape, providers must move beyond reactive billing and adopt proactive, standardized, and technology-enabled strategies. The following best practices reflect what high-performing DME organizations are doing in 2026 to protect revenue, reduce risk, and improve patient outcomes.
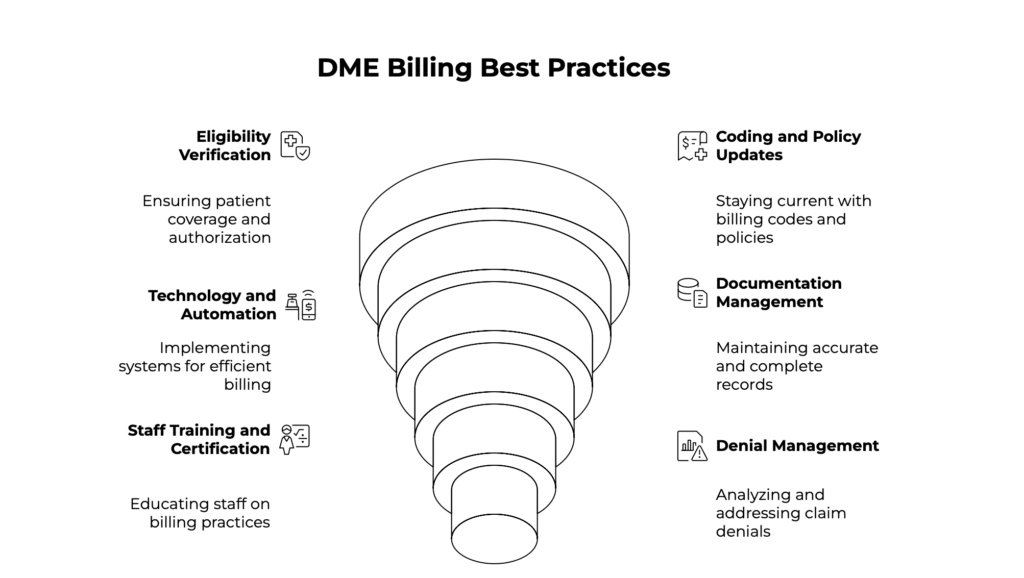
1. Implement Rigorous Eligibility Verification
Eligibility verification should begin as soon as an order is received and be rechecked prior to equipment delivery. Coverage details can change frequently due to policy updates, secondary insurance shifts, or patient status changes. This is especially critical for high-cost items and rental equipment, where reimbursement depends on strict compliance with payer rules.
Automated eligibility verification tools reduce manual effort and help staff identify coverage limitations, prior authorization requirements, and patient financial responsibility upfront. This minimizes surprise denials, improves patient communication, and prevents revenue loss tied to avoidable eligibility errors.
2. Stay Updated on Coding and Policy Changes
DME billing relies heavily on accurate HCPCS Level II coding and modifier usage, both of which are updated regularly by CMS and other payers. In 2026, mid-year policy changes and payer-specific rules are increasingly common, making outdated knowledge a major liability.
Ongoing education for billing and coding teams is essential. Regular training sessions, internal audits, and access to updated coding resources help ensure claims reflect the most current requirements. Staying current not only reduces denials but also strengthens compliance during audits and reviews.
3. Embrace Technology and Automation
Technology is no longer optional in DME billing. Modern practice management and billing platforms are designed to handle the complexity of DME workflows by automating high-risk and repetitive tasks, including:
Claim scrubbing before submission
Real-time eligibility validation
Intelligent code and modifier suggestions
Automated attachment of required documentation
These systems reduce human error, speed up claim processing, and improve first-pass acceptance rates. Over time, automation allows billing teams to focus less on rework and more on optimization, compliance, and strategic oversight.
4. Maintain Clean, Complete Documentation
Documentation is the foundation of every successful DME claim. Clinical notes, physician orders, proof of delivery, and medical necessity documentation must align clearly and consistently. Even minor issues — such as date mismatches, missing signatures, or unclear justification — can trigger denials or audits.
In 2026, payers increasingly expect documentation to be audit-ready at all times. Establishing standardized documentation workflows and routine internal checks helps ensure every claim tells a clear clinical story that supports medical necessity and payer requirements.
5. Train and Certify Staff Continuously
DME billing rules evolve quickly, and staff knowledge must evolve with them. Investing in continuous education ensures billing and coding teams remain confident, accurate, and compliant when handling complex claims.
Certification programs, role-specific training, and regular policy briefings help reduce guesswork and dependency on a few key employees. A well-trained team improves consistency, reduces costly mistakes, and strengthens the organization’s overall billing resilience.
6. Track Denial Trends and Respond Strategically
Denials should be treated as data, not just setbacks. Tracking denial reasons across payers, product categories, and workflows allows organizations to identify systemic issues rather than repeatedly fixing individual claims.
Using analytics or denial management dashboards helps uncover root causes such as documentation gaps, coding errors, or authorization failures. Addressing these issues at the process level leads to sustained improvements in clean claim rates and long-term revenue performance.
7. Prepare for Audits as Routine Practice
In 2026, audits are a standard part of DME operations rather than an exception. Medicare and commercial payers continue to expand both pre-payment and post-payment reviews, often using advanced analytics to select claims.
Organizations should maintain organized, easily retrievable records and ensure staff are trained to respond promptly and accurately to audit requests. Treating audit readiness as an everyday practice reduces stress, shortens response times, and demonstrates reliability and compliance to payers.
8. Evaluate Outsourcing and Specialist Support
For many DME suppliers, especially those experiencing growth or frequent policy changes, outsourcing billing functions or partnering with DME billing specialists can be a strategic advantage. External experts bring deep payer knowledge, dedicated compliance focus, and scalable resources that may be difficult to maintain internally.
Outsourcing can improve claim accuracy, reduce denial rates, and allow internal teams to focus more on patient service and operational growth. For some organizations, a hybrid approach — combining internal oversight with external expertise — delivers the best results.
Meet NikoHealth — Support for Your DME Billing Journey
As DME billing requirements continue to evolve, many suppliers are rethinking how they manage revenue cycle operations end to end. Having the right technology partner can make the difference between constantly reacting to denials and confidently scaling your business.
NikoHealth is built specifically for HME and DME providers, offering an all-in-one, cloud-based billing and business management platform designed to simplify complex workflows, improve accuracy, and support long-term growth.
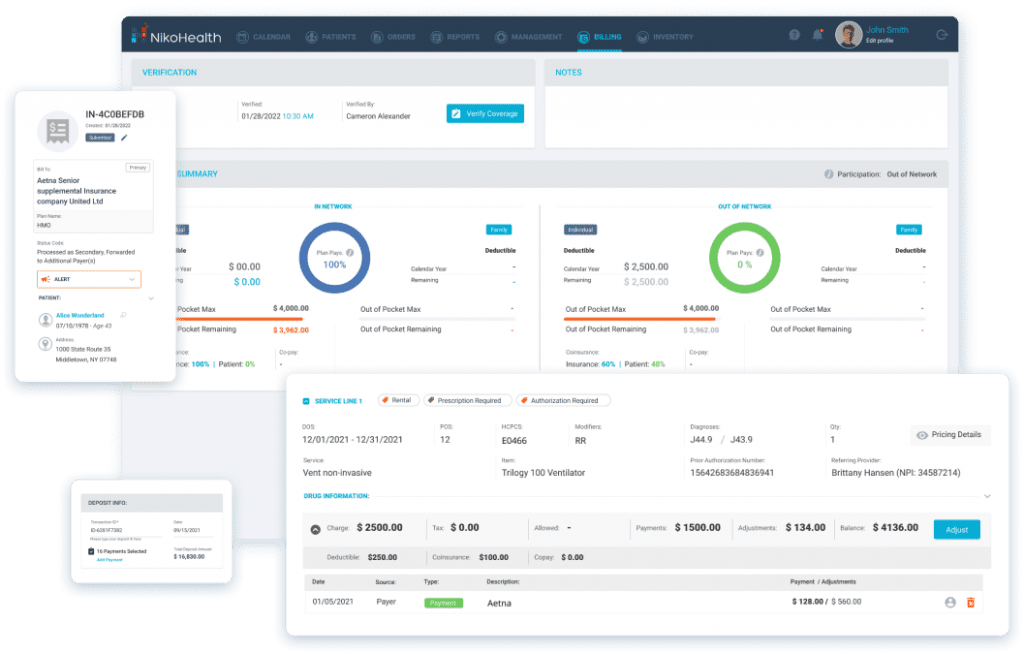
With NikoHealth, providers can:
Streamline billing and claims management with intelligent automation that helps ensure claims are clean, compliant, and submitted on time
Improve revenue capture and collections through automated eligibility verification, patient estimates, recurring rental billing, and payment posting
Reduce manual work and errors by eliminating repetitive touchpoints across order management, fulfillment, delivery, and billing
Stay audit-ready and compliant with payer-specific rules, documentation workflows, and real-time validation of billing requirements
Gain clear business insights using robust analytics that highlight denial trends, payer performance, and reimbursement timelines
Designed to be intuitive and easy to use, NikoHealth enables teams to onboard quickly, work efficiently from anywhere, and focus more time on patients — not paperwork. As billing complexity increases in 2026, having a unified platform helps DME organizations stay agile, compliant, and in control of their revenue cycle.
Conclusion
DME billing isn’t just transaction processing — it’s a specialized blend of clinical accuracy, coding expertise, regulatory compliance, and technology-enhanced operations. In 2026, the stakes are higher than ever: denials, audits, and shifting payer policies are the norm, but proactive practices and a culture of continuous improvement set successful providers apart.
By embracing automation, staying current with code and policy changes, and investing in training and documentation discipline, your organization can protect revenue, enhance patient satisfaction, and thrive in a dynamic healthcare ecosystem.
If you’d like help auditing your DME billing workflow or adopting best-in-class tools, the NikoHealth team is here to guide you.







Related Articles